
It excludes safety stock and other inventory types kept in case your cycle inventory runs dry. The specific identification method involves tracking the cost of each inventory item separately and assigning the specific cost to each unit sold. It provides precise cost information for each unit sold but requires extensive record-keeping and may not be practical for all businesses. The weighted average method calculates the average cost of all items in inventory and assigns this average cost to each unit sold. This method is useful when individual identification of inventory items is not practical or necessary.
What is Inventory Accounting? How It Works, Types of Inventory Accounting, and More

Instead, inventory counts are conducted periodically (usually at the end of a set financial period), such as annually or quarterly. These are just a few examples of the merchandise that a retail clothes store may handle. Each sort of inventory serves a distinct purpose and necessitates careful management to maximise stocking levels, save costs, and satisfy customer demands. Inventory refers to a company’s goods and products that are ready to sell, along with the raw materials that are used to produce them.
- This method is useful when individual identification of inventory items is not practical or necessary.
- And with less time spent chasing down answers to inventory tracking mysteries, you can free yourself up to spend more time growing your business.
- This method applies the double-entry accounting principle and provides a more accurate indication of a business’s current financial position.
- In other words, it’s all the stock that still has to go through manufacturing.
- It’s important to keep accurate inventory records to assist with inventory control and keep accurate balance sheets.
- Inventory refers to assets a business owns that are either in the form of goods ready for sale or will be converted into such goods.
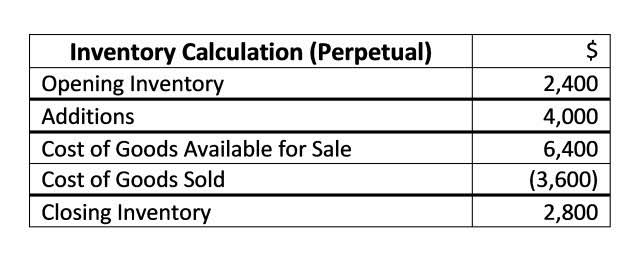
The Cost of Goods Sold
Further, the raw materials are divided into direct and indirect raw materials. Such classification would decide the manner in which the raw materials would be accounted for in the books of accounts. Thus, businesses across the world add value by types of inventory accounting refining and processing the raw material into something more useful. This increase in value enhances the price of the finished good and makes manufacturing activity profitable for the businesses. Further, you decide on the method using which the raw materials would be processed once such materials are selected.

types of inventory stored off-premises
Obsolete inventory, also called dead stock, refers to finished goods that are unable to be sold. Accountants need to determine whether to use first in, first out (FIFO), last in, first out (LIFO), weighted average method, or specific identification method of inventory accounting. If older inventory is less expensive, and you use it first, you would choose the FIFO accounting method. Or, you could assume that you used the most recent, most expensive inventory using the LIFO accounting method.
Raw Materials
- Inventory accounting plays a crucial role in accurately valuing and managing a company’s inventory assets.
- Inventory encompasses all the parts and raw materials a business uses or sells.
- By automating data capture and updating, businesses can maintain accurate inventory records and streamline inventory accounting processes.
- Possessing a high amount of inventory for a long time is usually not a good idea for a business.
- WIP inventory refers to any goods or materials which are part-way through the manufacturing process but haven’t yet been converted into a finished product.
The accounting treatment for raw materials depends upon whether they are direct Accounting For Architects or indirect raw materials. That is, how such materials would be recorded in the income statement and balance sheet of your company. For example, if you are a company manufacturing toys, you would need plastic as raw material.
Raw Materials and Finished Products
- This indicator, often called stock turnover, measures how much and how frequently a company’s inventory is sold, replaced, or used.
- In business, the inventory may be defined as the goods held for sale in the ordinary course of business or the goods that are used to manufacture goods to be sold.
- Furthermore, inventory adjustments are made by businesses to match the current level of inventory to match a product’s actual on-hand quantity.
- Although the basics of inventory control come naturally to many businesses, accurately tracking and recording inventory costs can be a real challenge.
- These systems can automate inventory tracking, generate real-time reports, and integrate with accounting systems for seamless financial record-keeping.
A mistaken inventory count can make it look as though a company has done more or less business than it actually has, affecting both its current and future overall valuation. A reliable stocktaking procedure allows businesses to know its inventory count and value, not only informing decision-makers and driving operations. Inventory accounting methods are the ways in which revenue and expenses are recorded – more specifically, when they are recorded. Let’s put the COGS formula into practice, since this is an especially important part of the inventory accounting process. Before we dive into the details, here’s a quick recap of some of the key terms and inventory accounting formulas you should know.

In a car factory, a vehicle frame with attached wheels but no engine would be WIP inventory. The JIT system reduces holding costs by ensuring stock levels closely match demand, which can minimise waste as inventory does not sit idle. Essentially, the reorder point considers the product’s usage rate and the lead time needed to replenish the stock, alongside the safety stock, if any. The reorder point ensures that an order is placed in time Accounting Periods and Methods to maintain stock availability and customer satisfaction. Implementing an ABC inventory system helps in identifying which items need more facility resources and tighter controls and which items require less attention. This system leads to better decision-making regarding purchasing, warehousing, and selling, resulting in cost and process optimisations.
Addressing common challenges—like human errors, shrinkage, and seasonal variability—proactively is essential for sustainable inventory management. Businesses that prioritise strong inventory practices, adopt advanced technologies, and remain flexible to market changes will achieve long-term success. Manually verify stock levels to ensure recorded data matches physical inventory, reducing discrepancies. Calculates inventory value using an average cost per unit, suitable for uniform products. Assumes newer inventory is sold first, useful during inflation for aligning higher costs with current revenues. This formula evaluates the percentage of inventory sold relative to what was received, indicating sales performance and stock efficiency.
 Skip to content
Skip to content

